What is vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D a lack indicates that your body is not getting enough vitamin D to keep healthy. It primarily affects your bones and muscles.
Why do I require vitamin D, and how can I obtain it?

Vitamin D increases in the absorption of calcium by the body. Calcium is an essential component in the development of bone.. Vitamin D also has a role in your neurological, muscular, and immune systems. Vitamin D can be obtained in three ways: through your skin, through your diet, and through a dietary supplement
What is the significance of vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for healthy body function, including bone health and immunity. It may even help prevent cancer and several chronic illnesses, such as
- bone loss
- type 2 diabetes
- heart disease
- multiple sclerosis
- depression
What causes vitamin D deficiency?
- having dark skin
- being older
- having overweight or obesity
- You can become vitamin D deficient for a variety of causes, including:
- You don’t get proper vitamin D in your daily diet.
- You don’t absorb enough vitamin D from food (a malabsorption problem) • You don’t get enough sunlight
- Your liver or kidneys can’t convert vitamin D to its active form in the body • You take medicines that interfere with your body’s ability to convert or absorb vitamin D
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin D deficiency has previously been related to rickets, a bone ailment. This syndrome can significantly damage the structural integrity of the bone, eventually leading to fractures. Aside from Rickets, vitamin D deficiency causes a slew of other diseases and problems, including asthma, various lung diseases, and a rain of cardiovascular diseases.
Common vitamin D deficiency symptoms include:
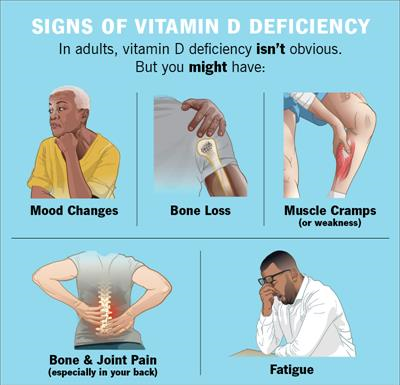
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Back Pain
- Bone Pain
- Frequent infections
- Slow-healing wounds
- Cramps and muscle pain
- Weakness in the muscles
- Mood changes or mood swings
Treatment/Prevention
How can you boost your vitamin D levels? While certain foods contain vitamin D, getting enough from sunlight is the best approach to prevent vitamin D deficiency symptoms.
However, research suggests that absorbing foods high in vitamin D and calcium helps you acquire more, so try including high-quality, natural sources in your diet on a regular basis.
Importance of Sunlight Exposure:
If you are fair to medium-toned, most experts recommend obtaining 10 to 15 minutes of direct sunlight per day without sunscreen. If you have dark skin, you probably need to spend more time outside to get enough vitamin D because you have more natural protection against UV radiation.

Some specialists advise darker-skinned persons to spend 40 minutes to an hour in the sun every day, if possible.
In the winter, you should double the recommended time to ensure enough vitamin D production.
Here’s a solid rule of thumb for determining whether or not your body is producing vitamin D:
- You want to look at your shadow and notice that it is shorter than you are. This indicates that the UV index is high enough.
- The UV index is normally maximum between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m.
If you are concerned about not wearing sunscreen and developing skin cancer, apply sunscreen to your face and hands but not your limbs straight away (assuming your limbs are exposed). This leaves enough exposed skin to produce enough vitamin D.
Increase your levels naturally by doing the following things and eating the following foods:
- Sunlight exposure: Aim for 10-20 minutes of sun exposure per day.
- Cod liver oil (approximate one tablespoon daily)
- Whitefish
- Swordfish
- Rainbow trout
- Pastured eggs
- Raw milk
How can you quickly increase your vitamin D level? Vitamin D supplements are separated into two types: D2 and D3.
D3 made up of animal products (particularly, cholesterol) is the most similar to the form produced by humans. Vitamin D3 is thus the more active form and is thought to convert significantly faster than D2.


