Aedes mosquitoes transmit the flu-like illness dengue.
Dengue infection is typicallysymptomless in its victims. However, it can also lead to a feverish condition, and in rare instances, dengue can cause people to become extremely ill, require hospitalization, or even cause them to pass away.

The dengue virus is the cause of dengue fever, a mosquito-transmitted tropical disease.Three to fourteen days after infection, symptoms usually start to appear. High temperature, nausea, headaches, pain in the muscles and joints, as well as the typical skin rash and itching may be among these symptoms. Recovery often takes two to seven days. In just a few percent of patients, the illness progresses into a more serious dengue hemorrhagic fever that causes bleeding, low blood platelet counts, and blood plasma leakage, or dengue shock syndrome, which results in a dangerously low blood pressure level..
Symptoms of Dengue Fever:-
- During infection, symptoms may appear four to six days later and linger for up to ten days.:
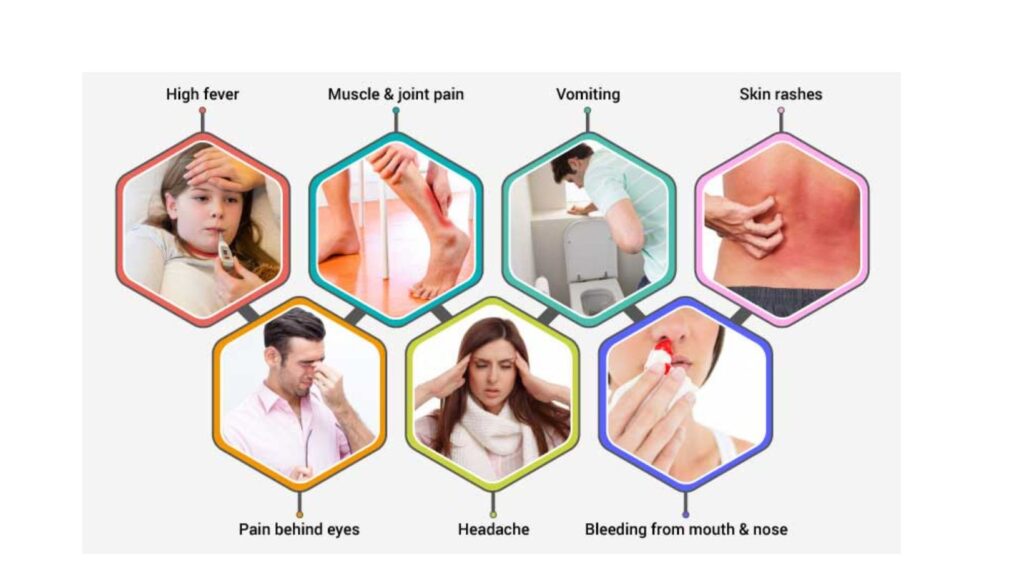
- Sudden, high fever (105 degree)
- Severe headaches
- Pain behind the eyes
- Severe joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Skin rash, which appears two to five days after the onset of fever
- Mild bleeding (such a nose bleed, bleeding gums, or easy bruising)
In a week or so, most people are back to normal. On sometimes, symptoms can become fatal and worsen. Dengue hemorrhagic fever, dengue shock syndrome, or severe dengue are additional names for this condition
Severe dengue is defined by damaged blood vessels that leak. The quantity of platelets in your blood that aid in clotting also declines. Organ failure, internal blood loss, shock, and even death could occur as a result of this.
Causes:-
Any one of the four dengue viral types might result in dengue fever. Being in close contact to someone who has dengue fever won’t cause you to contract it. Instead, mosquito bites are the primary method of transmission for dengue disease.
The two mosquito species that spread dengue viruses most frequently happen inside and outside of dwellings. The dengue virus enters a mosquito when it bites a person who suffers with it. After that, the virus enters the bloodstream of the person who is bitten by the infected mosquito and produces an infection.
After you have recovered from dengue fever, you have lifetime immunity to the virus type that caused your infection, but not to the other three dengue fever virus types. This implies that you could contract the infection once more in the future.
Treatment of Dengue Fever:-
There are currently no established treatments or particular medications to treat dengue infection. The doctor may generally advise taking paracetamol rather than aspirin to control the pain and fever and consuming more fluids to prevent bleeding. Until and until specifically prescribed by a doctor, aspirin should not be given to children under the age of 12.
In severe cases, hospitalization for 24 hours, intravenous (IV) fluid supplementation, and blood transfusions are necessary.
Prevention of Dengue Fever:-
The patient has to get enough sleep in bed, especially on the days when the fever is at its worst. They should also take time off of work, school, childcare, or preschool.
Dengue patients should stay at home until they are no longer dangerous (around 3-5 days), and they should avoid areas where they could be bitten by mosquitoes.
As the Aedes mosquito prefers to reproduce in stagnant, clean water that can be found openly close to human habitats, ensure your surrounds are free of any water logging problems to prevent this illness.
The Dengue virus has not yet been protected against by a vaccination. Avoiding mosquito bites is the only means of prevention.
- Cover your skin by wearing long pants, and long-sleeved shirts.
- Use of mosquito repellents, traps, and nets.
- Keep all the doors and windows closed especially at dawn, dusk, and early evening to avoid the entry of Dengue mosquitoes.
- Keep your surroundings clean by removing all the waste and cleaning the standing water.


